class g airspace on sectional chart
Made using AFMAN 11-202v3 dated 10 June 2020 and a bunch of random sources on the internet. Class E Airspace exists at 1200 AGL unless otherwise designated as shown above.

Faa Regulations Is The Airspace At Kgpt Class E Or G When The Tower Is Closed Aviation Stack Exchange
This is where the Class E Airspace extends from surface level all the way up to 17999 feet.

. Class b airspace map. Since drones likely arent capable of reaching these altitudes a drone pilot need not be concerned with Class A airspace. In general it is uncontrolled airspace outside of the ATC system surrounding non-towered airports and ending where Class E airspace begins normally 700ft AGL to 1200ft AGL.
Sectional Chart Representation. Class G airspace within the United States extends up to 14500 Mean Sea Level MSL. On the sectional aeronautical chart Class G Airspace is depicted as shown on Figure 2.
Air Traffic Control Facility. Were a stones throw from the massive NYC Class Bravo and the entire NY metro area can get very busy. When Class E Airspace extends down to the surface the sectional shows a faded magenta line thats the 700 AGL to 17999 MSL but will also show a dashed red circle.
Class A airspace exists between the range of 18000 feet and 60000 feet. This line shows enroute Class E airspace starting at. Therefore any pilot encountering the See Chart Supplement for DEsurf eff hrs label on any VFR sectional chart is forced to check the Chart Supplement or other resources to understand the status of the surface-level airspace when the tower is closed.
No communication or transponder is required and the weather requirements tend to be less in Class G depending on time of day. Airspace boundaries are depicted with solid blue lines. Class G airspace can be somewhat confusing to new pilots.
11142012 80046 PM. Use with caution but I do feel good about the research I did on. Class G airspace is not depicted on any chart.
However class g is not represented on a sectional chart. The reason we put that in bold is because it is likely to appear on your written exam. Minimum flight visibility and distance from clouds.
Almost all of the high class G airspace has been eliminated by airspace changes through the regulatory process completed during the last 12 months. 14 rows Class G airspace will always start at the ground and go up to 14500 msl as a maximum. And its always exclusive.
Differentiates floors of Class E Airspace greater than 700 ft. Class G airspace uncontrolled is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as Class A Class B Class C Class D or Class E airspace. Airspace types because on sectional charts it may be marked with a dashed magenta line a shaded magenta line or a shaded blue line.
Surface-level controlled airspace converts to Class G airspace when the tower is closed. To begin with Class G Ground is the uncontrolled by ATC layer of airspace that covers the surface and whose ceiling generally goes up to 1200ft in open areas. Furthermore although the FAA AIM states that Class E airspace begins at 14500 feet MSL unless noted otherwise in most areas in the US.
Class EG Sectional Chart Airspace Question. Around airports can drop to 700ft and even the surface. 1200 or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude.
Daytime requirements for Class G are 1 statute mile. Understanding airspace is really important around Danbury as we have a lot of heavy-duty airspace very close to our airport. Pilots are always encouraged to keep up to date sectional charts to stay on top of the changes.
On sectional chart solid blue lines. Airspace On Sectional Charts Author. Numbers show top and bottom of airspace in hundreds of feet so 30 means 3000ft 100 10000ft SFC stands for surface.
4 5 3 Figure 2 The magenta shaded area 4 represents the Transition Zone and encloses an area in which Class G Airspace extends from the surface up. The legend though doesnt indicate what the vertical limits of controlled airspace would have been in those days. A stronger line far left on the image above is used to emphasize outer boundary of B class airspace.
Finally there is special use airspace depicted on the sectional charts in various ways. Greg Bockelman Jan 28 2021 7. Class a is airspace from 18000ft msl up to 60000ft msl fl600 and atc clearance along with an ifr flight plan is required to enter class a.
Might as well make it all Class E to 700 feet. Class A Not Depicted on Sectional Charts IFR Only Private Pilot 18000 to 60000 MSL Referred to as Flight Level in Hundreds of Feet Eg FL 350 35000. Class E Airspace low altitude Federal Airways are indicated by center line.
Discussion in Pilot Training started by Trogdor Jan 28 2021. For example if Class E starts at 700 feet AGL Class G goes up to but doesnt include 700 feet AGL. On the sectional aeronautical chart Class G Airspace is depicted as shown on Figure 2.
Intersection - Arrows are directed towards facilities which establish. On a map Class Gs ceiling is the floor of Class E airspace. Class B airspace refers to the airspace surrounding the countrys busiest airports including major air travel hubs in New York Chicago and Los Angeles.
The extent of Class B airspace typically reaches up to 10 nautical miles from the airport and can have two or more. Class G airspace is most easily found on a sectional map when a fading thick blue line appears. The extent of Class B airspace typically reaches up to 10 nautical miles from the airport and can have two or more.
Class B Bravo Airspace. Way out in the rural unpopulated areas the ceiling goes up to 14500ft. In most cases the airspace overlying Class.
In all reality Class G airspace always ends well before 14500 msl due to another layer of airspace being on top of it. Class E Airspace is controlled airspace and youll need to have authorization to fly here. In accordance with FAR 91155.
Class G is uncontrolled airspace generally underneath and is exclusive of the Class E airspace above it. This airspace is typically used by commercial airlines for long-haul flights. That little sliver of airspace is useless as Class G airspace.
Surface that abuts Class G Airspace. Rules governing VFR flight have been adopted to assist the pilot in meeting the responsibility to see and avoid other aircraft. Generally from surface up to 4000 feet msl including the airspace above the horizontal boundary up to 10000 feet msl.
In this 1957 sectional chart all controlled airspace was shaded. Apr 10 2014. Class G airspace is most easily found on a sectional map when a fading thick blue line appears.
Class E airspace is likely the most unique among all US. Heres a small portion of the New York Sectional showing my home airport of DXR click for a larger version.

Class E And G Airspace Youtube
Airspace Guide Usa Chart Reading Tutorial C Aviation
Questions About Class E G Airspace Dji Phantom Drone Forum

Faa Regulations What Would Be The Airspace Class When No Vignette Is Visible On A Us Vfr Sectional Chart Aviation Stack Exchange
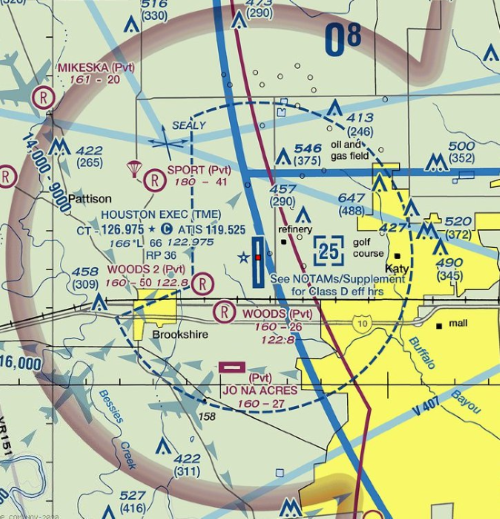
Class G Airspace Explained By A Commercial Pilot

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod

Airspace Charting Question Pilots Of America

Usa What Are Concrete Examples For Class G Up To 14500 Aviation Stack Exchange

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod
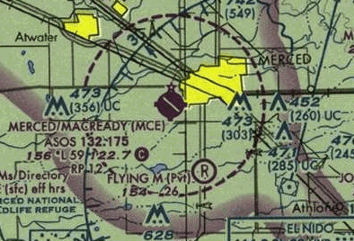
Lookout Mountain Flight Park Hang Gliding And Paragliding In Chattanooga Tn
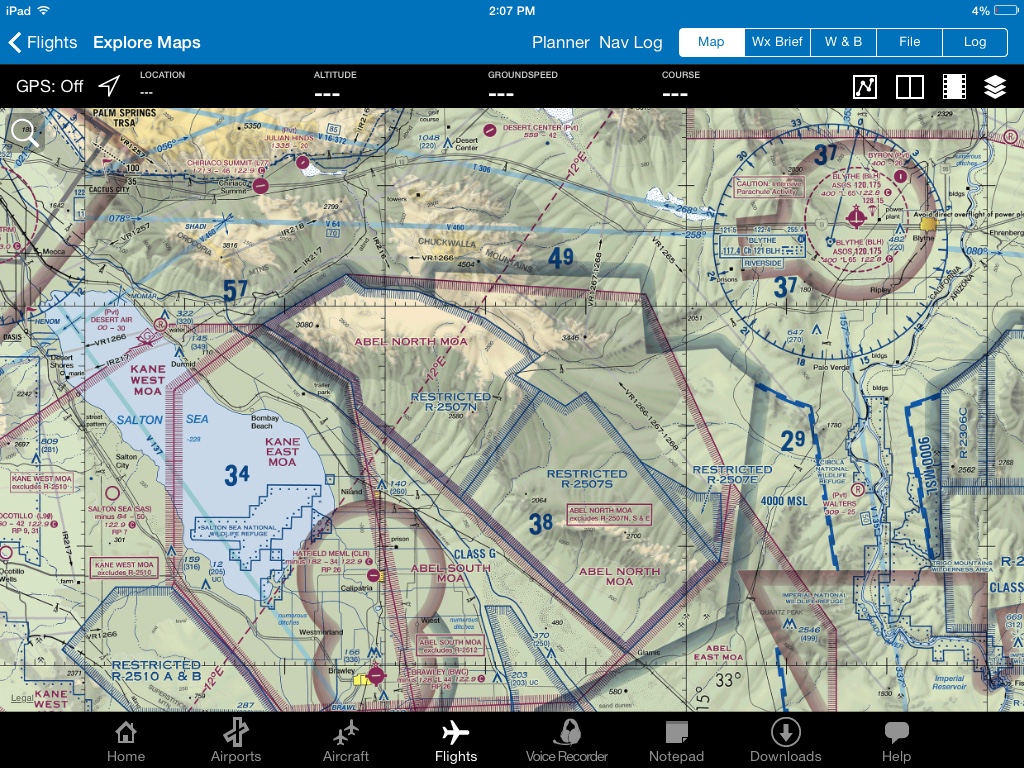
Class G And E Airspace Pilots Of America

Airspace Colors Sectional Charts

How Do You Know When Class E Airspace Starts At 700 Feet Agl Vs 1 200 Feet Agl Drone Pilot Ground School

Practice Question Refer To Figure 26 What Airspace Is Tomlinson Airport In Drone Pilot Ground School

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod

John Class C Airspace Is Nothing To Be Afraid Of All It Takes Is Some Preparation And Good Commu Aviation Education Good Communication Skills Fear Of Flying

Usa What Are Concrete Examples For Class G Up To 14500 Aviation Stack Exchange

